Java异常机制(Exception)

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public class A {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new A().a();
}
public void a(){
b();
}
public void b(){
a();
}
}
|

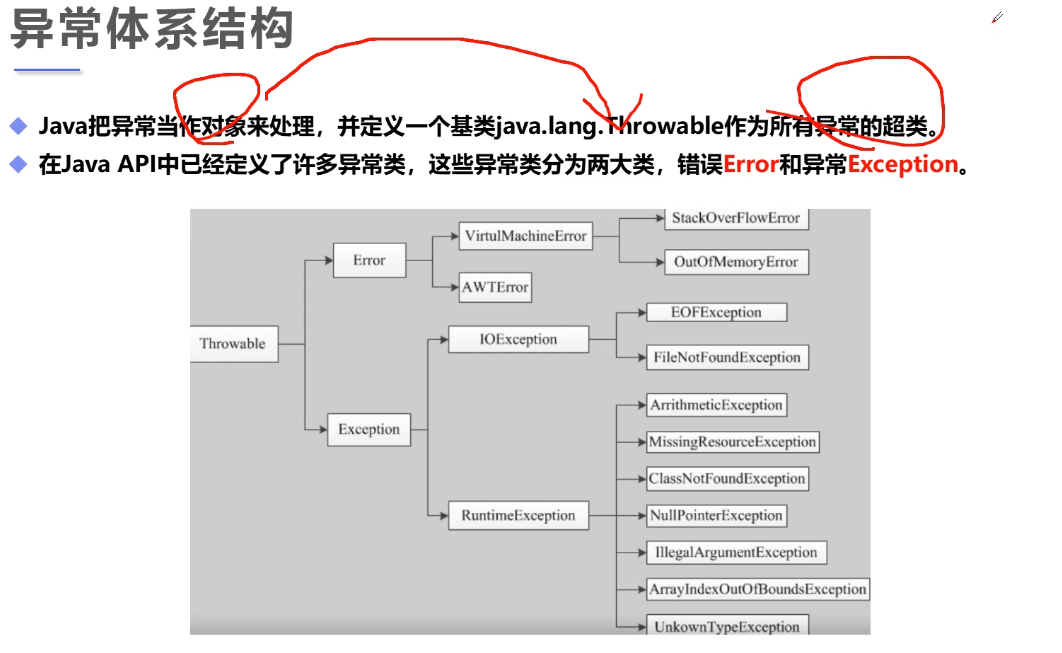
错误(Error)与异常(Exception)

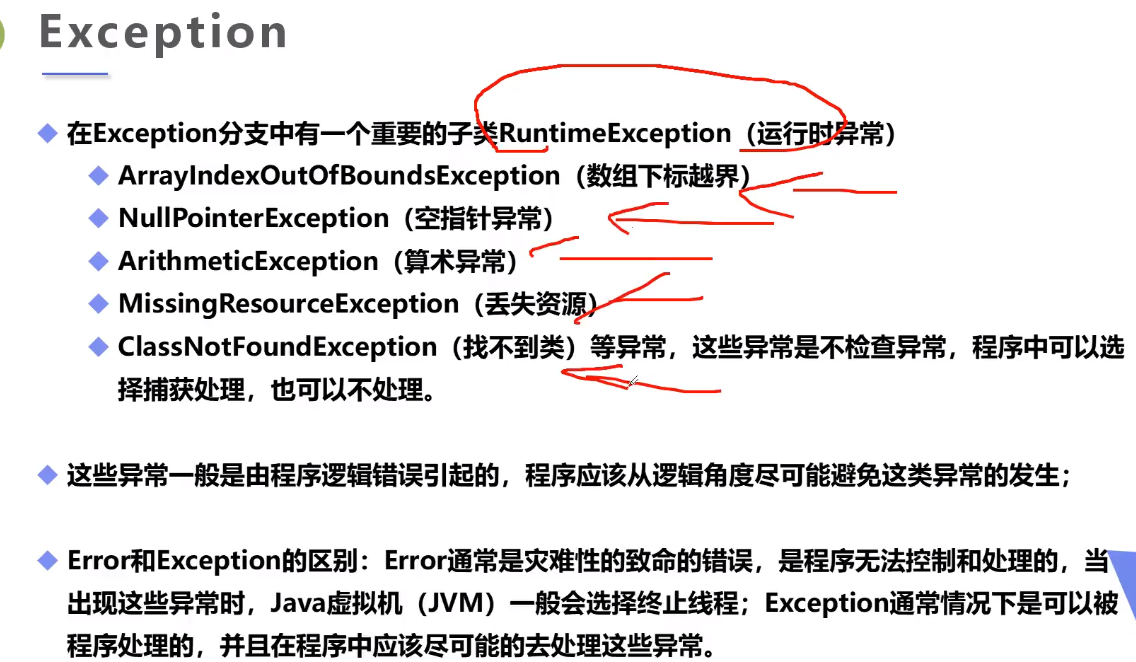
Exception可以分成运行时异常和非运行时异常。
从继承关系可知:Throwable是异常体系的根,它继承自Object。Throwable有两个体系:Error和Exception,Error表示严重的错误,程序对此一般无能为力,例如:
OutOfMemoryError:内存耗尽NoClassDefFoundError:无法加载某个ClassStackOverflowError:栈溢出
而Exception则是运行时的错误,它可以被捕获并处理。
某些异常是应用程序逻辑处理的一部分,应该捕获并处理。例如:
NumberFormatException:数值类型的格式错误FileNotFoundException:未找到文件SocketException:读取网络失败
还有一些异常是程序逻辑编写不对造成的,应该修复程序本身。例如:
NullPointerException:对某个null的对象调用方法或字段IndexOutOfBoundsException:数组索引越界
Exception又分为两大类:
RuntimeException以及它的子类;- 非
RuntimeException(包括IOException、ReflectiveOperationException等等)
Java规定:
- 必须捕获的异常,包括
Exception及其子类,但不包括RuntimeException及其子类,这种类型的异常称为Checked Exception。
- 不需要捕获的异常,包括
Error及其子类,RuntimeException及其子类。
以上理论只作为了解内容,重点是如何处理异常。
异常处理(抛出与捕获)

所有异常都可以调用printStackTrace()方法打印异常栈,这是一个简单有用的快速打印异常的方法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
int b = 0;
try {
System.out.println(a/b);
}catch (ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("程序异常,变量b不能为0");
}finally{
System.out.println("finally");
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
new Test().a();
}catch (Throwable e){
System.out.println("Exception");
}
}
public void a(){
b();
}
public void b(){
a();
}
}
|
try-catch...-catch结构:一般把较大的异常放在后面。
假设要捕获多个异常,必须从小到大,否则会报错!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
int b = 0;
try {
System.out.println(a/b);
}catch (Error e){
System.out.println("Error");
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println("Exception");
}catch (Throwable t){
System.out.println("Throwable");
}
finally{
System.out.println("finally");
}
}
}
|
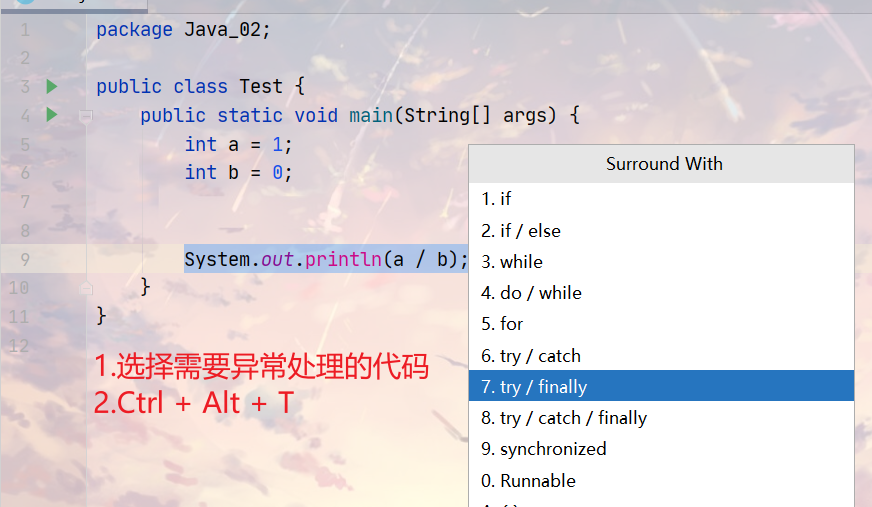
IDEA异常处理快捷键:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
new Test().test(1,0);
} catch (ArithmeticException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void test(int a,int b) throws ArithmeticException{
if (b == 0) {
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
}
}
|
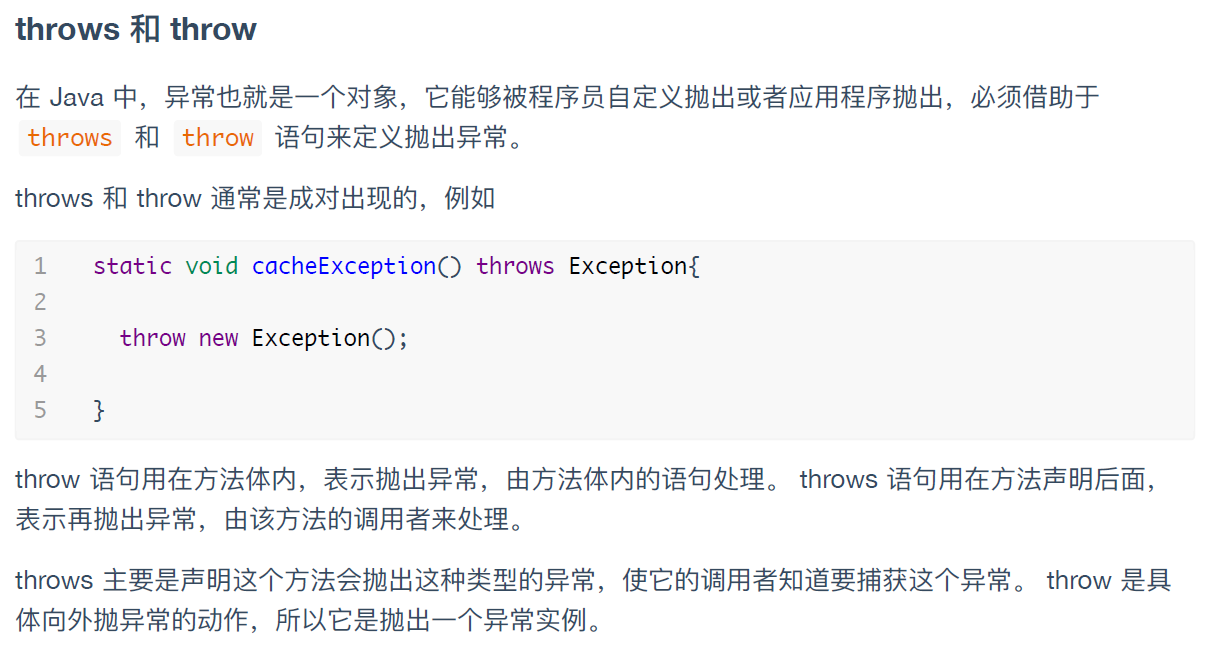
throws声明这个方法可能会抛出异常,throw语句是实际的抛出异常的语句。
异常处理的一般经验:捕获那些你知道如何处理的异常,继续传播(抛出)那些不知道如何处理的异常。
自定义异常
大部分情况下,我们不需要自定义异常。

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
public class MyException extends Exception{
private int detail;
public MyException(int a) {
this.detail = a;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "MyException{" +
"detail=" + detail +
'}';
}
}
public class Test {
static void test(int a) throws MyException{
System.out.println("传递的参数为:"+a);
if (a>10){
throw new MyException(a);
}
System.out.println("OK");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
test(1);
test(11);
} catch (MyException e) {
System.out.println("MyException=>"+e);
}
}
}
|

IDEA代码出现波浪线(一些异常等),按住Alt + Enter进行处理。











