4.习题 4.1 acwing.1219. 移动距离 第六届蓝桥杯省赛C++B组,第六届蓝桥杯省赛JAVAA/C组
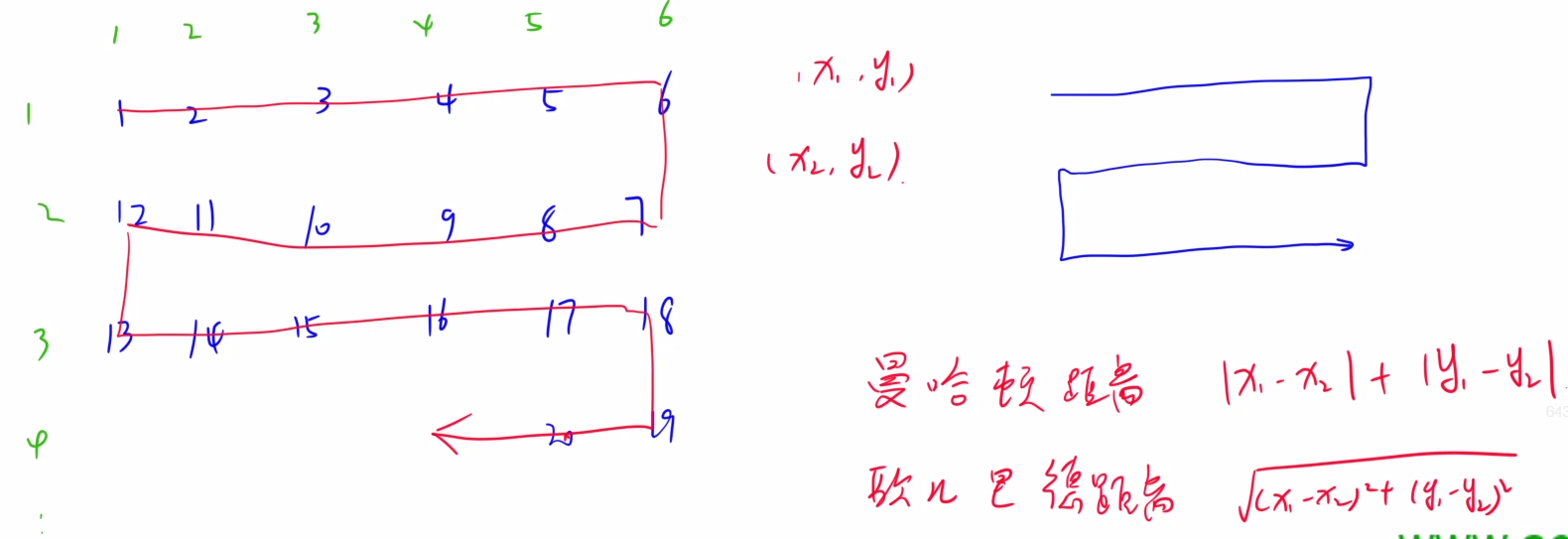
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 X星球居民小区的楼房全是一样的,并且按矩阵样式排列。 其楼房的编号为 1 ,2 ,3 … 当排满一行时,从下一行相邻的楼往反方向排号。 比如:当小区排号宽度为 6 时,开始情形如下: 1 2 3 4 5 6 12 11 10 9 8 7 13 14 15 .....我们的问题是:已知了两个楼号 m 和 n,需要求出它们之间的最短移动距离(不能斜线方向移动)。 输入格式 输入共一行,包含三个整数 w,m,n,w 为排号宽度,m,n 为待计算的楼号。 输出格式 输出一个整数,表示 m,n 两楼间最短移动距离。 数据范围 1 ≤w,m,n≤10000 ,输入样例: 6 8 2 输出样例: 4
思路:
算法题中涉及到的距离一般分为两种:曼哈顿距离与欧几里得距离。
曼哈顿距离在语法课中介绍过了,欧几里得距离就是直线距离。
本题要求的就是曼哈顿距离。
处理编号时,我们全部都减去1,这样每一行编号对宽度w取模是相同的值。
如果不处理,假设第一行是1到6,那么它们模6的结果是0,0,0,0,0,1,需要特殊处理。
这也是C++为什么很多地方下标都从0开始的原因之一。
行号和列号以及编号都设定为从0开始。
接下来的问题就是如何表示大楼的行号和列号,
很容易得到:分别是n/w和行号%2 ? w-1-n%w : n%w。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std ;int n,m,w;int main () cin >> w >> n >> m; n--,m--; int x1 = n/w,x2 = m/w; int y1 = n%w,y2 = m%w; if (x1%2 ) y1 = w-1 -y1; if (x2%2 ) y2 = w-1 -y2; cout << abs (x1-x2) + abs (y1-y2) << endl ; return 0 ; }
4.2 acwing.1229. 日期问题 第八届蓝桥杯省赛C++B组,第八届蓝桥杯省赛JAVAB组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 小明正在整理一批历史文献。这些历史文献中出现了很多日期。 小明知道这些日期都在1960 年1 月1 日至2059 年12 月31 日。 令小明头疼的是,这些日期采用的格式非常不统一,有采用年/月/日的,有采用月/日/年的,还有采用日/月/年的。 更加麻烦的是,年份也都省略了前两位,使得文献上的一个日期,存在很多可能的日期与其对应。 比如02 /03 /04 ,可能是2002 年03 月04 日、2004 年02 月03 日或2004 年03 月02 日。 给出一个文献上的日期,你能帮助小明判断有哪些可能的日期对其对应吗? 输入格式 一个日期,格式是”AA/BB/CC”。 即每个’/’隔开的部分由两个 0 -9 之间的数字(不一定相同)组成。 输出格式 输出若干个不相同的日期,每个日期一行,格式是”yyyy-MM-dd”。 多个日期按从早到晚排列。 数据范围 0 ≤A,B,C≤9 输入样例: 02 /03 /04 输出样例: 2002 -03 -04 2004 -02 -03 2004 -03 -02
思路:
和回文日期非常像。
我们可以直接按给定的日期范围进行枚举,把日期看成是整数。
先判断日期是否合法,再判断是否满足题目要求。
简单计算一下,日期范围内大概一百万个数,<10^6。
因为我们是从小到大枚举的,所以输出的时间肯定是从早到晚排列的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std ;int days[13 ] = {0 ,31 ,28 ,31 ,30 ,31 ,30 ,31 ,31 ,30 ,31 ,30 ,31 };bool check_valid (int year,int month,int day) if (month == 0 || month > 12 ) return false ; if (month != 2 ){ if (day == 0 || day > days[month]) return false ; } else { int leap = year%4 ==0 && year%100 || year%400 == 0 ; if (day > 28 +leap) return false ; } return true ; } int main () int a,b,c; scanf ("%d/%d/%d" ,&a,&b,&c); for (int date = 19600101 ;date <= 20591231 ;date++){ int year = date/10000 ,month = date%10000 /100 ,day = date%100 ; if (check_valid(year,month,day)){ if (year%100 == a && month == b && day == c || month == a && day == b && year%100 == c || day == a && month == b && year%100 == c){ printf ("%d-%02d-%02d\n" ,year,month,day); } } } return 0 ; }
还有一种思路,就是根据读入的日期,直接反推合理的日期,但是还要判断日期是否合法,还要按大小排序,
时间复杂度可以控制到O(1),但是可能写起来很麻烦,所以这里还是用暴力但简单的做法。
附上大佬题解:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <vector> using namespace std ;struct Date { int y, m, d; bool operator < (const Date &t)const { if (y != t.y) return y < t.y; if (m != t.m) return m < t.m; return d < t.d; } bool operator == (const Date &t)const { return y == t.y && m == t.m && d == t.d; } }; vector <Date> date;int a[3 ];const int days[13 ] = {0 , 31 , 28 , 31 , 30 , 31 , 30 , 31 , 31 , 30 , 31 , 30 , 31 };bool check (int y, int m, int d) if (y < 1960 || y >= 2060 || m < 1 || m > 12 ) return false ; int maxd = days[m]; if (m == 2 && (y % 400 == 0 || (y % 4 == 0 && y % 100 ))) maxd++; if (d < 1 || d > maxd) return false ; return true ; } int main () string s; cin >> s; a[0 ] = (s[0 ] - '0' ) * 10 + s[1 ] - '0' ; a[1 ] = (s[3 ] - '0' ) * 10 + s[4 ] - '0' ; a[2 ] = (s[6 ] - '0' ) * 10 + s[7 ] - '0' ; if (check(1900 + a[0 ], a[1 ], a[2 ])) date.push_back({1900 + a[0 ], a[1 ], a[2 ]}); if (check(2000 + a[0 ], a[1 ], a[2 ])) date.push_back({2000 + a[0 ], a[1 ], a[2 ]}); if (check(1900 + a[2 ], a[0 ], a[1 ])) date.push_back({1900 + a[2 ], a[0 ], a[1 ]}); if (check(2000 + a[2 ], a[0 ], a[1 ])) date.push_back({2000 + a[2 ], a[0 ], a[1 ]}); if (check(1900 + a[2 ], a[1 ], a[0 ])) date.push_back({1900 + a[2 ], a[1 ], a[0 ]}); if (check(2000 + a[2 ], a[1 ], a[0 ])) date.push_back({2000 + a[2 ], a[1 ], a[0 ]}); sort(date.begin(), date.end()); date.erase(unique(date.begin(), date.end()), date.end()); for (int i = 0 ; i < date.size(); i++) printf ("%d-%02d-%02d\n" , date[i].y, date[i].m, date[i].d); return 0 ; } 作者:NumPy 链接:https: 来源:AcWing 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
补充知识点:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 ------ string its (int x) stringstream ss;ss << x; string s;ss >> s; return s;} ----- int sti (string s) stringstream ss;ss << s; int x;ss >> x; return x;} ----- bool is (int y) return (y % 4 == 0 && y % 100 != 0 || y % 400 == 0 );}
4.3 acwing.1231. 航班时间 第九届蓝桥杯省赛C++A组,第九届蓝桥杯省赛JAVAA组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 小 h 前往美国参加了蓝桥杯国际赛。 小 h 的女朋友发现小 h 上午十点出发,上午十二点到达美国,于是感叹到“现在飞机飞得真快,两小时就能到美国了”。 小 h 对超音速飞行感到十分恐惧。 仔细观察后发现飞机的起降时间都是当地时间。 由于北京和美国东部有 12 小时时差,故飞机总共需要 14 小时的飞行时间。 不久后小 h 的女朋友去中东交换。 小 h 并不知道中东与北京的时差。 但是小 h 得到了女朋友来回航班的起降时间。 小 h 想知道女朋友的航班飞行时间是多少。 对于一个可能跨时区的航班,给定来回程的起降时间。 假设飞机来回飞行时间相同,求飞机的飞行时间。 输入格式 一个输入包含多组数据。 输入第一行为一个正整数 T,表示输入数据组数。 每组数据包含两行,第一行为去程的起降时间,第二行为回程的起降时间。 起降时间的格式如下: h1:m1:s1 h2:m2:s2 h1:m1:s1 h3:m3:s3 (+1 ) h1:m1:s1 h4:m4:s4 (+2 ) 第一种格式表示该航班在当地时间h1时m1分s1秒起飞,在当地时间当日h2时m2分s2秒降落。 第二种格式表示该航班在当地时间h1时m1分s1秒起飞,在当地时间次日h2时m2分s2秒降落。 第三种格式表示该航班在当地时间h1时m1分s1秒起飞,在当地时间第三日h2时m2分s2秒降落。 输出格式 对于每一组数据输出一行一个时间hh:mm:ss,表示飞行时间为hh小时mm分ss秒。 注意,当时间为一位数时,要补齐前导零,如三小时四分五秒应写为03 :04 :05 。 数据范围 保证输入时间合法(0 ≤h≤23 ,0 ≤m,s≤59 ),飞行时间不超过24 小时。 输入样例: 3 17 :48 :19 21 :57 :24 11 :05 :18 15 :14 :23 17 :21 :07 00 :31 :46 (+1 )23 :02 :41 16 :13 :20 (+1 )10 :19 :19 20 :41 :24 22 :19 :04 16 :41 :09 (+1 )输出样例: 04 :09 :05 12 :10 :39 14 :22 :05
思路:
首先要了解时差、时区的概念。
飞行时长计算公式:
往西飞,飞行的时长是相差+时差。往东飞,飞行的时长是相差-时差。
区时计算公式:
计算的区时=已知区时-(已知区时的时区-要计算区时的时区)
这题重点在于处理输入,需要记住一些技巧。
第一步,先将所有时间转化成距离当天00:00:00的秒数,一天大概86400秒。这样方便后续加减计算。
第二步,根据秒数再还原成时间,利用%和/运算。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <string> #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> using namespace std ;int get_seconds (int h,int m,int s) return h*3600 + m*60 + s; } int get_time () string line; getline(cin ,line); if (line.back() != ')' ) line += " (+0)" ; int h1,m1,s1,h2,m2,s2,d; sscanf (line.c_str(),"%d:%d:%d %d:%d:%d (+%d)" ,&h1,&m1,&s1,&h2,&m2,&s2,&d); return get_seconds(h2,m2,s2) - get_seconds(h1,m1,s1) + d*24 *3600 ; } int main () int n; scanf ("%d" ,&n); string line; getline(cin ,line); while (n--){ int time = (get_time() + get_time()) / 2 ; int hour = time/3600 ,minute = time%3600 /60 ,second = time%60 ; printf ("%02d:%02d:%02d\n" ,hour,minute,second); } return 0 ; }
sscanf的用法:
从一个字符串中读进于指定格式相符的数据。利用它可以从字符串中取出整数、浮点数和字符串。
sscanf和scanf的区别:scanf是以键盘作为输入源,sscanf是以字符串作为输入源。
函数原型:int sscanf(const char *str, const char *format,......);
提示:以下代码存在风险,请谨慎参考!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ;int getTime (void ) int h1,m1,s1,h2,m2,s2,d=0 ; scanf ("%d:%d:%d %d:%d:%d (+%d)" ,&h1,&m1,&s1,&h2,&m2,&s2,&d); int time=d*24 *3600 +h2*3600 +m2*60 +s2-(h1*3600 +m1*60 +s1); return time; } int main () int t; scanf ("%d" ,&t); for (int i = 0 ; i < t; i++) { int time1=getTime(); int time2=getTime(); int t=(time1+time2)/2 ; printf ("%02d:%02d:%02d\n" , t/3600 , t/60 %60 , t%60 ); } return 0 ; }